IoT Protocol -- Modbus
OSI vs. Modbus Layers:

Tip:
- RS-485/RS485’s new name is EIA-485.
- UART usually (99%) means TTL in shops, not 232/485.
- DB9 physical port usually (90%) means 232 electrical signals level standards.
Modbus Protocol #
See Also:
- 【strongly recommend!】 a nice intro to Modbus and Modbus Enron. (Simply Modbus 软件收费,但是这个 Modbus 入门文档非常好)
- 一文看懂 Modbus 协议
- Complete Modbus Guide.
- a good intro to Modbus.
Each Modbus Slave has 4 tables with 9999 values in each table.
| Coil/Register Number (//≈index) | Data Addresses | Table (//Abbreviation &) Name | Tab.的中文“区块”名 | RW Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-9999 | 0000 ~ 270E | (DO) Discrete Output Coils | 线圈状态 | (RW) Read-Write |
| 10001-19999 | 0000 ~ 270E | (DI) Discrete Input Contacts | 离散输入 | (RO) Read-Only |
| 30001-39999 | 0000 ~ 270E | (AI) Analog Input Registers | 输入寄存器 | (RO) Read-Only |
| 40001-49999 | 0000 ~ 270E | (AO) Analog Output Holding Registers | 保持寄存器 | (RW) Read-Write |
注意! Output is writable, input is read-only. This is master’s perspective!
2 tables for on/off discrete values (coils/contacts) 开关量离散值 (线圈/触点);
2 tables for numerical analog values (registers) 模拟量连续值 (保持寄存器).
1 coil/contact = 1 bit, addresses are from 0000 to 270E;
1 register = 1 word = 16 bits = 2 bytes, addresses are from 0000 to 270E.
Modbus Modes #
2 modes: ASCII (hex text string) vs. RTU (binary).
ascii #
Frame format (“冒号开始,回车结束”):
| Start | Address | Function | Data | LRC | End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| : | 2 Chars | 2 Chars | n Chars | 2 Chars | CR LF |
rtu #
(i.e. remote terminal unit)
Frame format:
| Start Silent | Slave ID/Address | Function | Data | CRC | End Silent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 char-time | 1 Byte | 1 Byte | n Byte | 2 Byte | 3.5 char-time |
DEF 从站地址 Slave ID: 【1st Byte】in Master’s requests, 1 ~ 247.
DEF 功能码 Function Code: 【2nd Byte】in Master’s requests, R/W Type & Table.
DEF 偏移量(Offset): Numbers (//≈index,点位地址) 与 Data Address (数据地址) 的差值是偏移量。四张表的(点位地址与数据地址的) 偏移量(offset)分别是 1, 10001, 30001 and 40001。
DEF CRC 校验 Cyclic Redundancy Check: 【last 2 Byte】 in every message.
| Function Code | Action | Table (//Abbreviation &) Name | 读写的(区块)表的中文名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Read | DO Discrete Output Coils | 读:线圈状态/离散输出/开关量输出 |
| 02 | Read | DI Discrete Input Contacts | 读:离散输入/开关量输入 |
| 03 | Read | AO Analog Output Holding Registers | 读:保持寄存器/模拟量输出 |
| 04 | Read | AI Analog Input Registers | 读:输入寄存器/模拟量输入 |
| 05 | Write single | DO Discrete Output Coil | 写:(单个)线圈状态/离散输出 |
| 06 | Write single | AO Analog Output Holding Register | 写:(单个)保持寄存器 |
| 0F (15 dec) | Write multiple | DO Discrete Output Coils | 写:(多个)线圈状态/离散输出 |
| 10 (16 dec) | Write multiple | AO Analog Output Holding Registers | 写:(多个)输入寄存器 |
special ones #
When changing unit address (such as to “2”, 0x02), the unit will confrim the change with the old address and use new address from next message. (ref)
问询(修改地址为 2):
| 地址码 | 功能码 | 起始地址 | 修改数值 | 校验码低位 | 校验码高位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0xFF | 0x06 | 0x07 0xD0 | 0x00 0x02 | 0x1D | 0x58 |
应答(回应修改):
| 地址码 | 功能码 | 起始地址 | 修改数值 | 校验码低位 | 校验码高位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01 | 0x06 | 0x07 0xD0 | 0x00 0x02 | 0x08 | 0x86 |
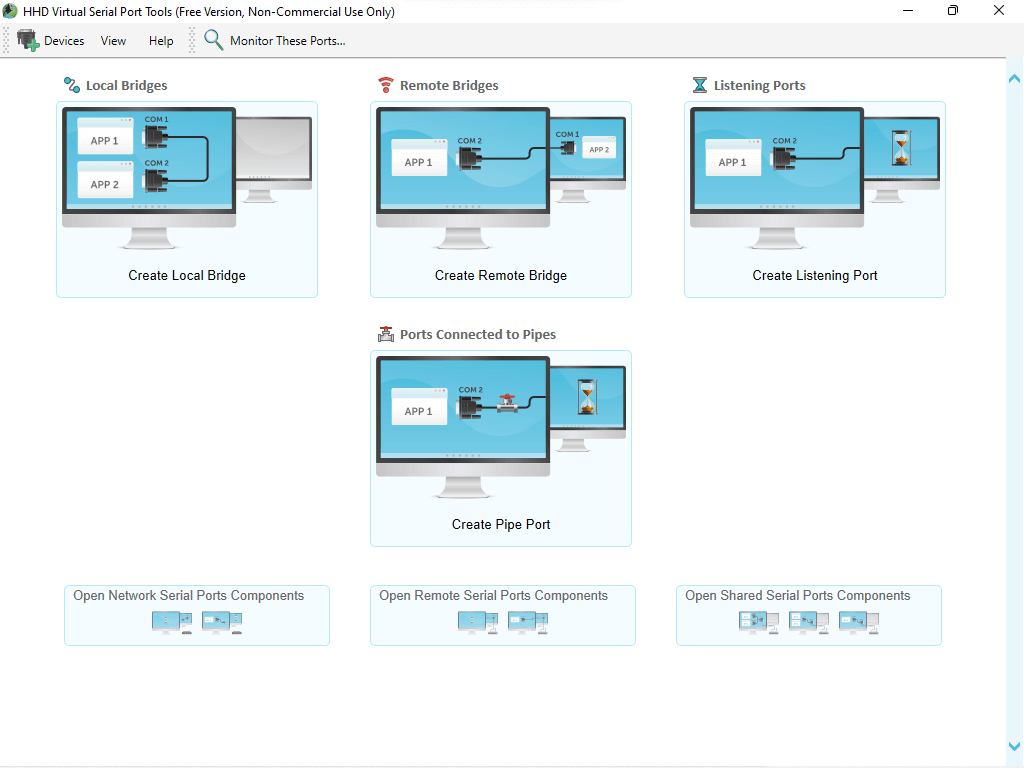
Serial Port/Line/Connection Simulator/Emulator Software/Tools #
- Note: Setup / Use (Write & Read) Linux serial ports require root permission
com0com / Null-modem emulator (windows, free) [suggested for win] #
- serial line/connections
a kernel-mode virtual serial port driver for Windows.
download from sourceforge

free virtual serial ports (windows, free & commercial) #
- serial line/connections
- free version limit: port not permanent
- commercial version: support remote virtual paired ports (based on samba?)
tty0tty (linux, free) [suggested for nix] #
- serial line/connections (pair of searial ports)
- need to compile (a bug is fixed by sunny)
https://gitcode.net/sino/tty0tty
The modem status lines are properly emulated, but the “termios” (行规程) settings are not.
virtual serial port driver /vspd (windows, commercial) #
- serial line/connections (pair of searial ports)
Suports 3 modes: null-modem / loopback, standard, customed wire connections.
14 天试用。汉化版: 虚拟串口驱动
vtty (linux, free) #
- serial line/connections (pair of searial ports) (not tested)
https://github.com/anszom/vtty
virtual serial port driver for linux / vspdl (linux, free) #
(having problems to install)
https://tibbo.com/support/downloads/vspdl.html
socat (linux, free, build-in) #
actually, not exactlly a good choice for my need.
Modbus Master & Slave Device Debug/Simulation/Emulation Software/Tools #
mthings (windows, free) [suggested for win] #
- in-app serial line/connections (TCP/UDP only, NO RTU, inside the software only).
- master & slave devices.
download
摩尔信使 MThings 串口 Modbus 模拟主机 入门 (5 分钟 B 站);
官方 B 站;
官方博客 CSDN;
基于 MThings 搭建模拟主机调试 MODBUS 从机设备.
基本操作 #

- 打开后主窗口如图,上部(偏左)的菜单(链接、数据、自定义等等)控制右侧(中间)显示相应子操作菜单和对应内容。
- 提示:“全部链接”默认即可;COM 口是从系统自动识别的,不需要“添加”,可能需要“刷新”;MODBUS-RTU 一般配置为无校验(无奇偶校验,因为已有 CRC)。
- 在右侧(偏中间)设置完“设备起始地址”和“设备结束地址”后,点击“添加”,然后选择本软件要“模拟主机”还是“模拟从机”,点击确定会自动添加两个地址(含)中间范围内所有的地址 所对应的“主机/上位机”或“从机”到左侧边栏。
- 中间左边,[M]表示 master/主机/上位机/client,[S]表示 slave/从机/server。
模拟主机读 #

在数据界面,点击“批量读”后,“同步至其他设备”意思是其他设备也批量读,“循环”选项也会被“同步”。

在数据界面,如果在“批量读”过程中点击“配置”,会停止当前地址(设备)数据的读取,但是不影响其他地址(设备)。即,此停止没有自动“同步”到其他设备。
模拟从机数据 #
Ref: 面包板 eet-china, (bak)
modbus poll & modbus slave (windows, commercial) #
- master (Modbus Poll) & slave (Modbus Slave) devices.
developed by Witte Software (modbustools.com).
modbus mechanic (java jar, thus cross-platform) [suggested for nix] #
- master & slave
- GUI & headless CLI
- RTU scanner
web & java JDK, github (gitee backup).
Requires: OpenJDK. Note: both jdk (tested openjdk 17.0.3, 2022-04-19) and modbusMechanic are pre-compiled.
Simple guide (requires two terminal windows):
# 1st terminal:
sudo java -jar ./ModbusMechanic.jar
# 2nd terminal:
./modpull -b 9600 -p none -m rtu -a 1 -r 1 -c 10 /dev/tnt6
Complete guide:
Add a slave/server with registers: select type (RTU is suggested, TCP also ok) & port & baud rate; Tools > Start Slave Simulator (can start many slave devices); setup a register & value type & a value and “Add” (can add many to one slave).
Read data:
Option 1. use ModbusMechanic: select type (RTU or TCP) & port & baud rate (canNOT be the port occupied by the slave simulator); set Slave-Node (station address) and Register; set value type; “Transmit Packet”.
Option 2. use other tools, such as modpoll from modbusdriver.com.

modbus-utils / libmodbus-dev #
- master & slave
cd ~
# download src & dev lib
sudo apt install libmodbus-dev
git clone https://github.com/Krzysztow/modbus-utils.git
# install option 1
$ cd modbus-utils
$ git submodule update --init
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
# OR:
# install option 2
cd modbus-utils/modbus_client
gcc -o modbus_client modbus_client.c -lmodbus -I/usr/include/modbus -I$HOME/modbus-utils/common
cd ../modbus_server
gcc -o modbus_server modbus_server.c -lmodbus -I/usr/include/modbus -I$HOME/modbus-utils/common
mbpoll (linux, free) #
- master only (not tested)
- CLI-only
- totally free but need to compile from source with some careness.
https://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/jammy/en/man1/mbpoll.1.html
lib: modbusdriver.com (cross-platform library, free & commercial) #
- master (modpoll) & slave (diagslave) demo & library
- commercial, 30-day free trial
Pro (free demo): for windows & linux; compile for multi-platforms.
Note: Slave (diagslave) provides fixed all-zero values.
Commercial lib with free master & slave demo:

More Modebus Tools #
- masters:
- free: QModMaster, Modbus Tester, Modpoll from proconX, RMMS (Radzio! Modbus Master Simulator).
- commercial: Simply Modbus Master (RTU and ASCII ), Modbus Poll from modbus tools, ModScan32 from WinTECH.
- slaves:
- free: ModRSsim2 was forked from MOD_RSSIM (Windows-based Modbus PLC Simulator), pyModSlave based on Qt (video tutorial).
- commercial: WinModbus (www.winmodbus.com), UnSlave Modbus Slave Simulator.
- libraries
- FreeMODBUS: free with separated ASCII/RTU and TCP.
- libmodbus: BSD 3-clause, for Linux, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, QNX and Win32.
- another list of useful tools
TTS vs. (EIA/TIA) RS 232 vs. 422 vs. 485 #
electrical signals level standards & common characteristics (电气电平规定和常见特性的区别) #


DB9 pin definition differences (DB9 物理接口定义区别) #

pic ref: 数据中心运维管理 in sohu, (bak)
232 485 422 电气标准、网络拓扑、速度速率 #
- 如下图, a b c 为典型错误接线方法,d e f 为(对应 a b c 情况时)典型正确接线方法。或采用集线器(aka 分配器)。

- 理论通信距离: RVSP 屏蔽双绞线(0.4 平) + 理想环境 + 100kbps (~115200bps) + 只有一台设备 = 1200 米。 距离乘以 n,速度除以 n (平衡双绞线的长度与传输速率成反比). ref (速度与距离关系,串口回环测试 etc.), bak
终端电阻 485 通信距离超过 300 米(尤其是总线上设备数量较少时),要在结束端(最远端)增加一个 120Ω 终端电阻(开始端可能也需要)。 (当设备数量较多时,例如超过 22 台,一般不需增加终端电阻,没有必要且降低负载能力)